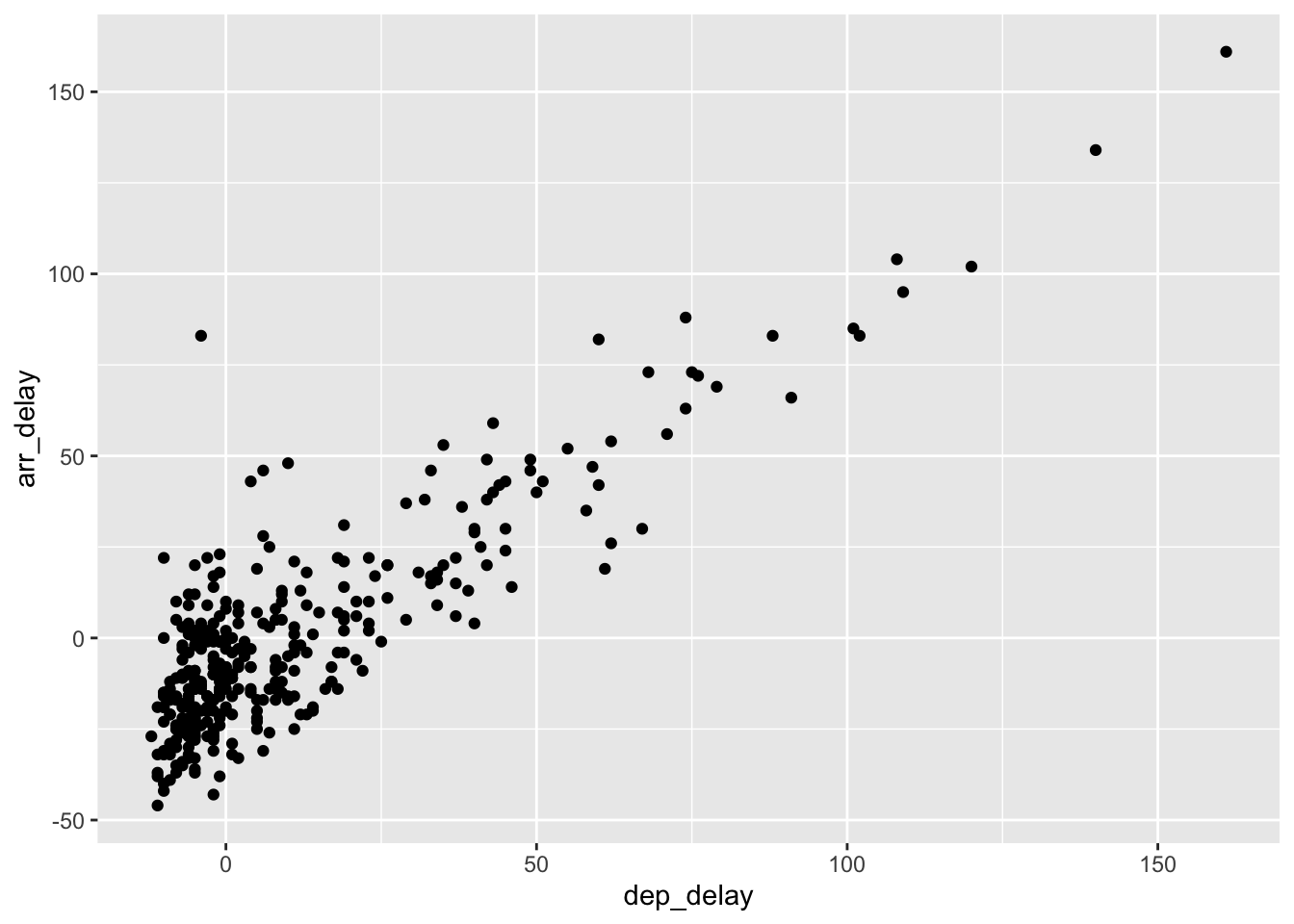
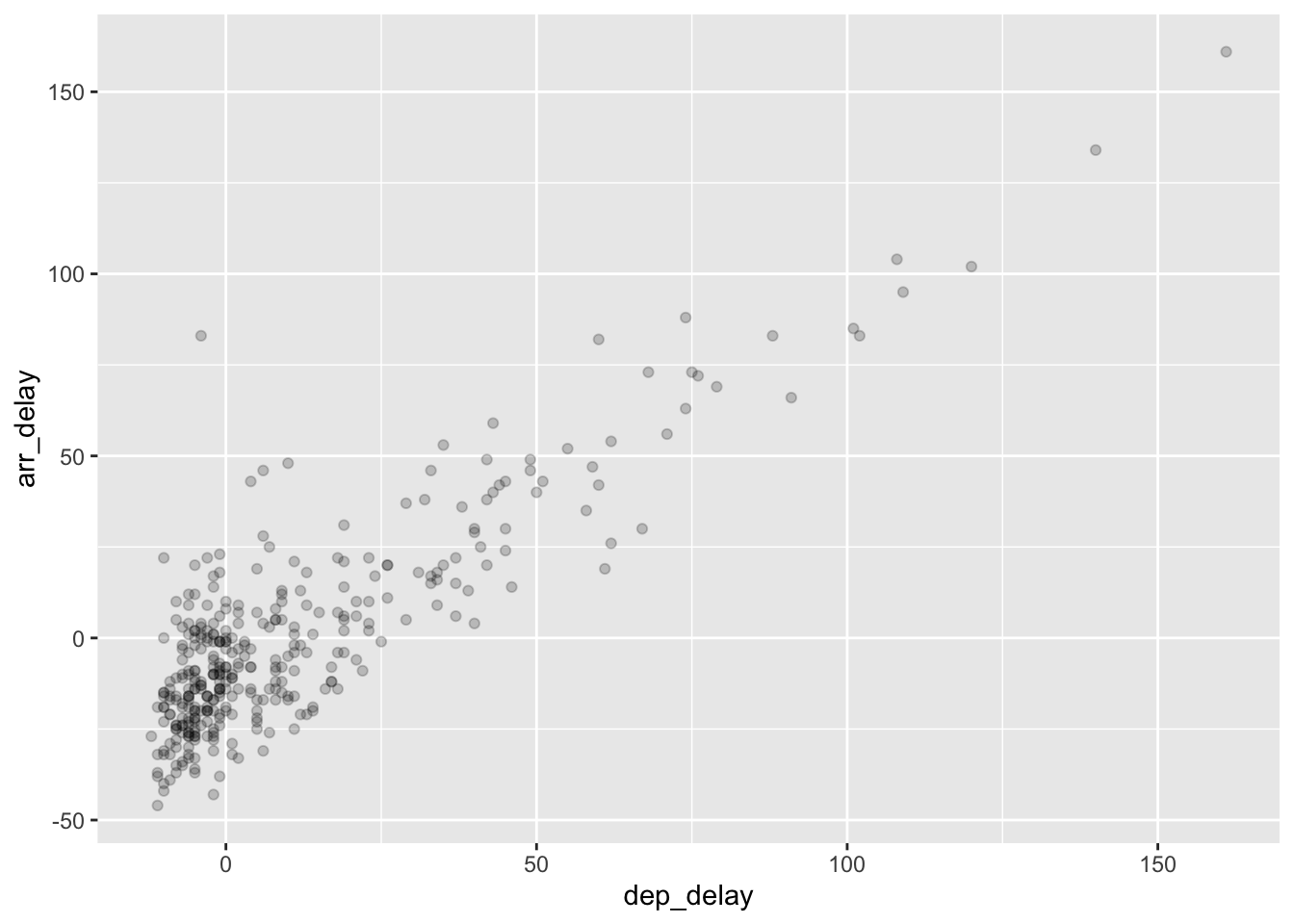
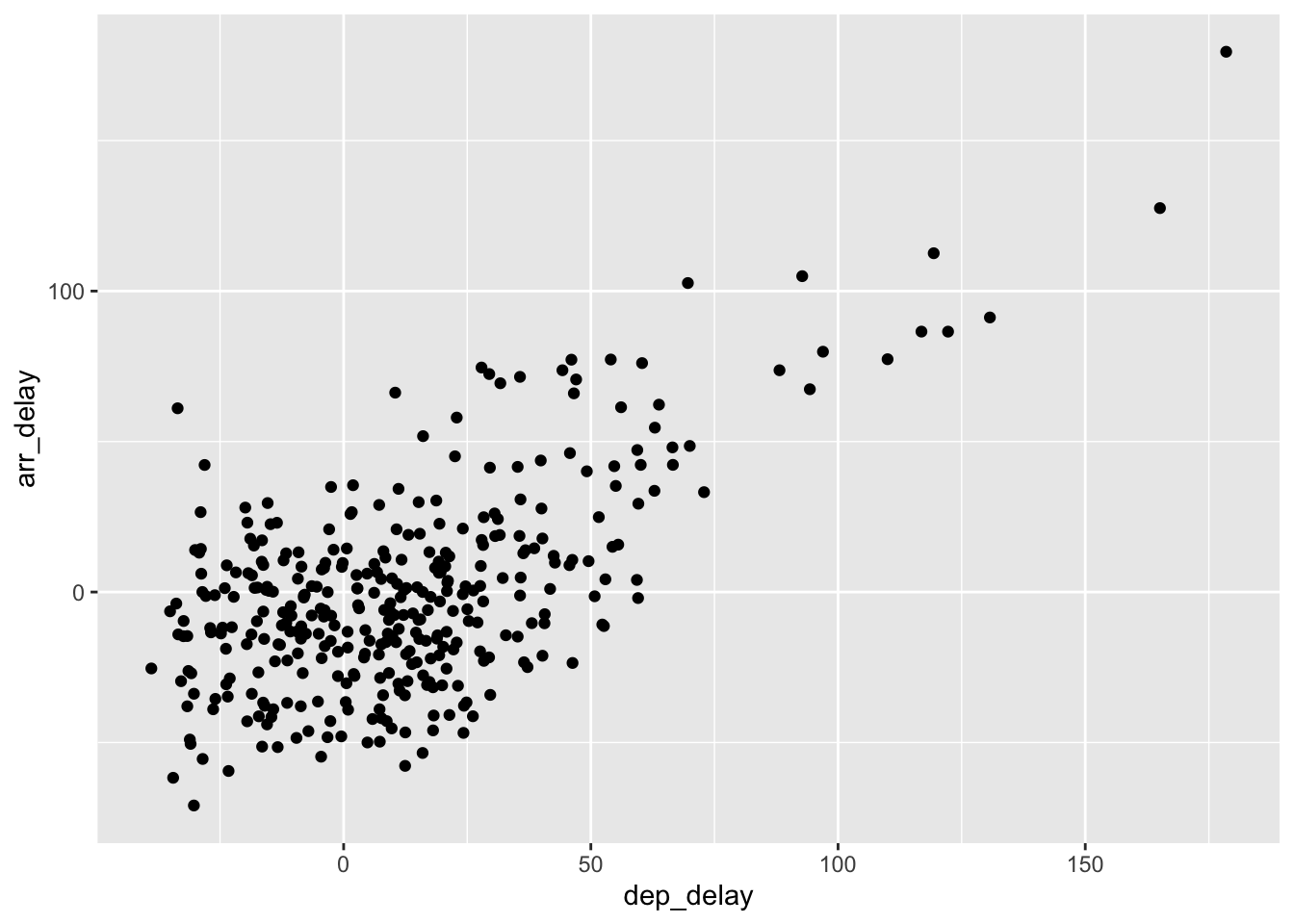
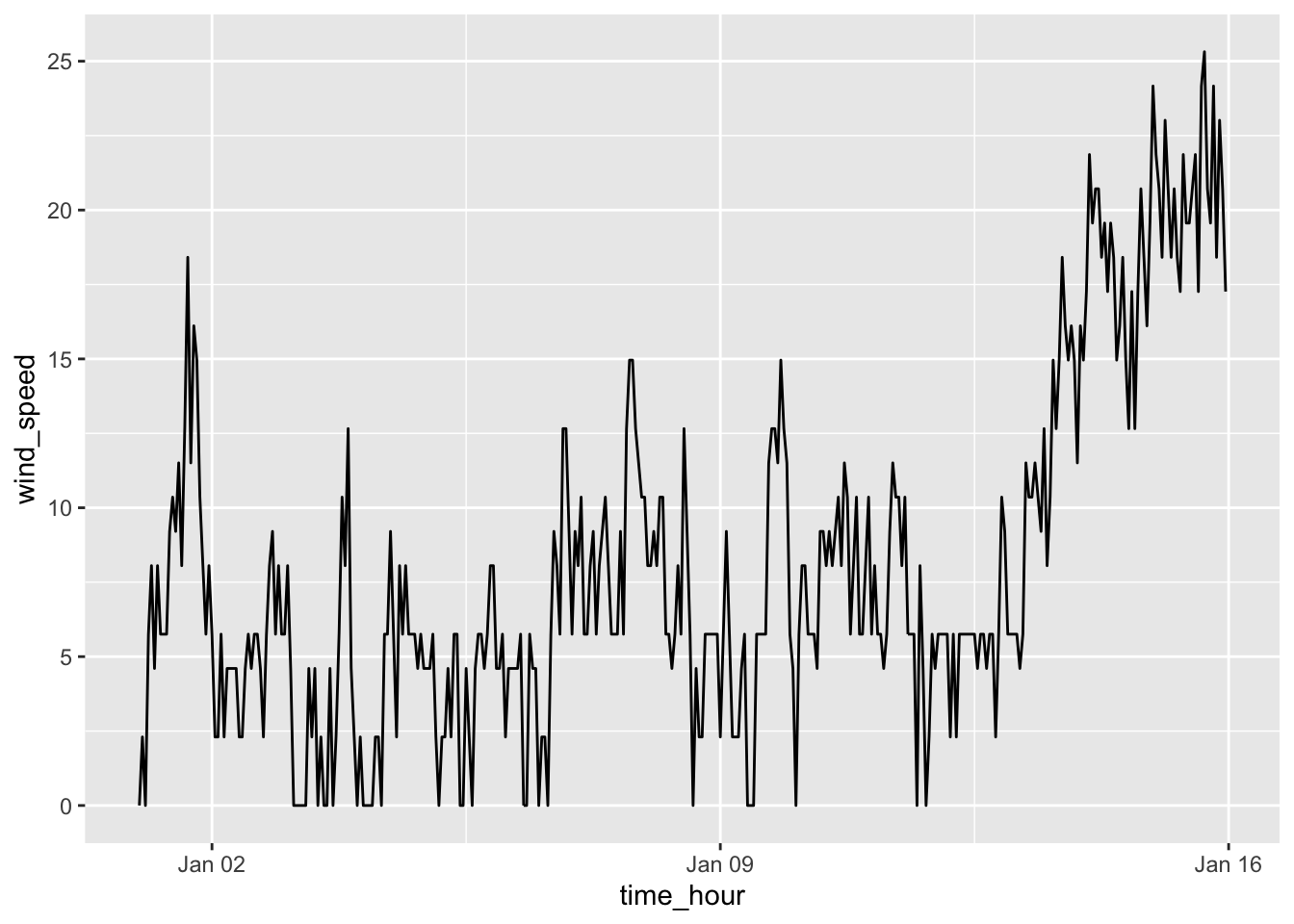
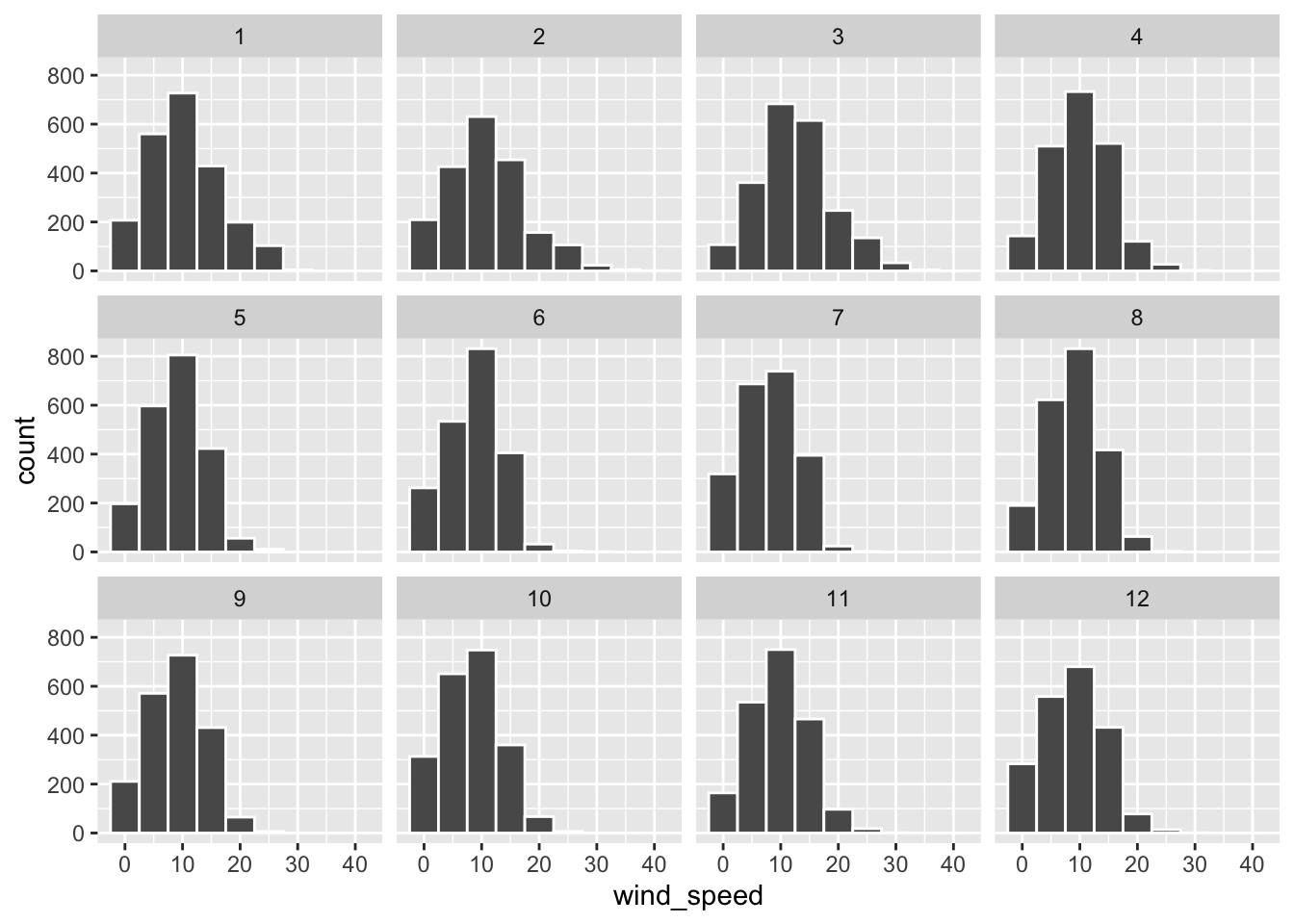
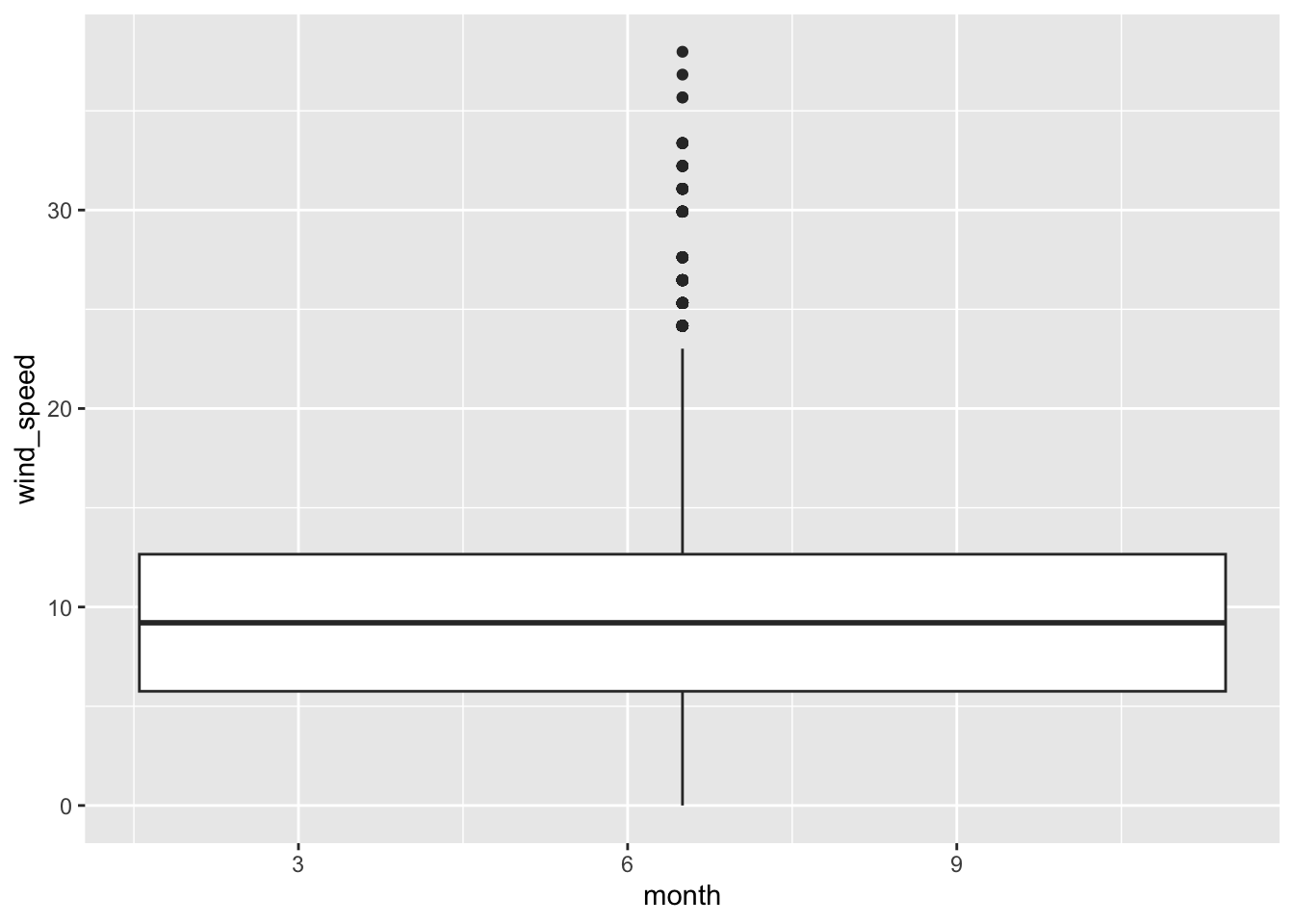
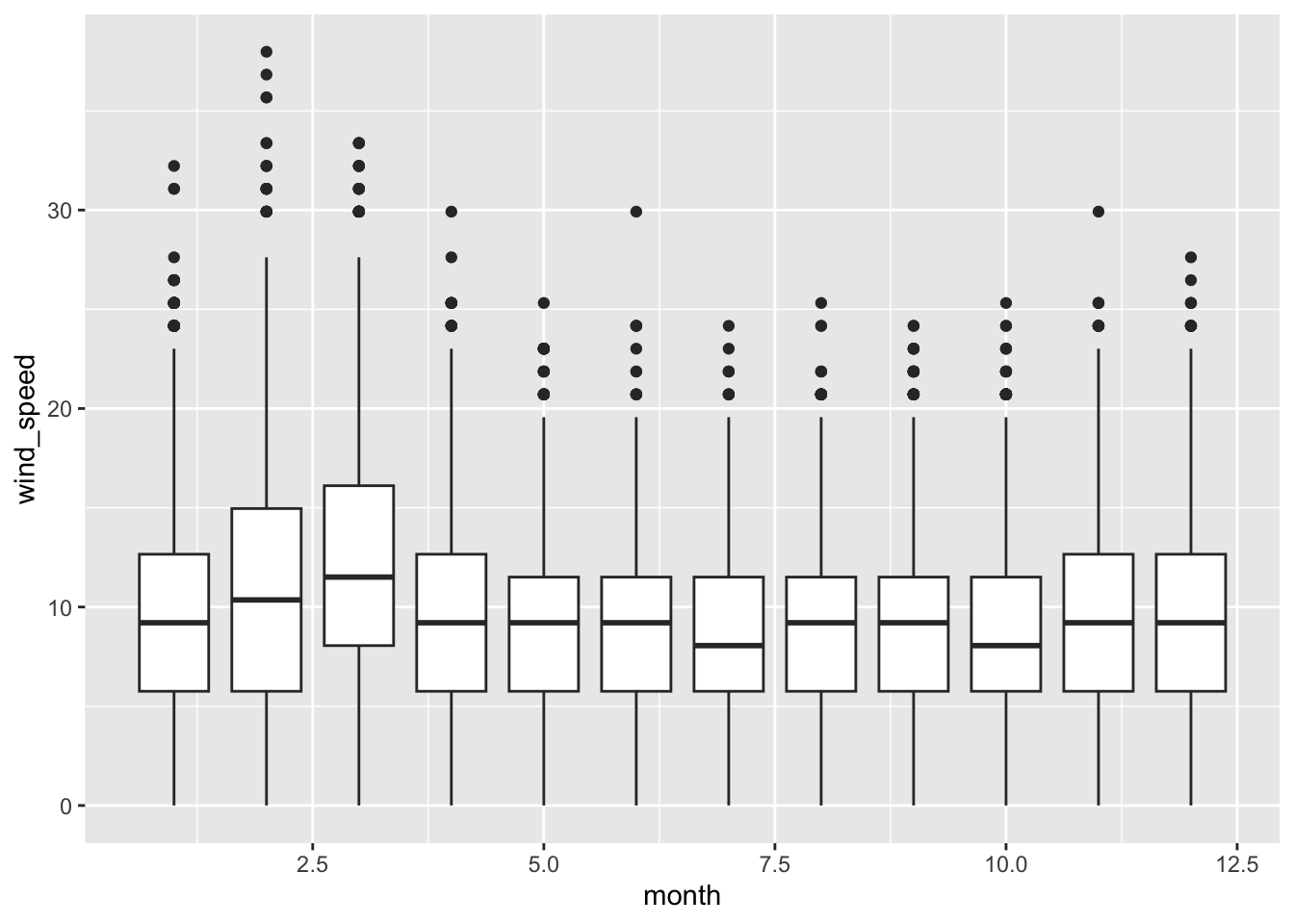
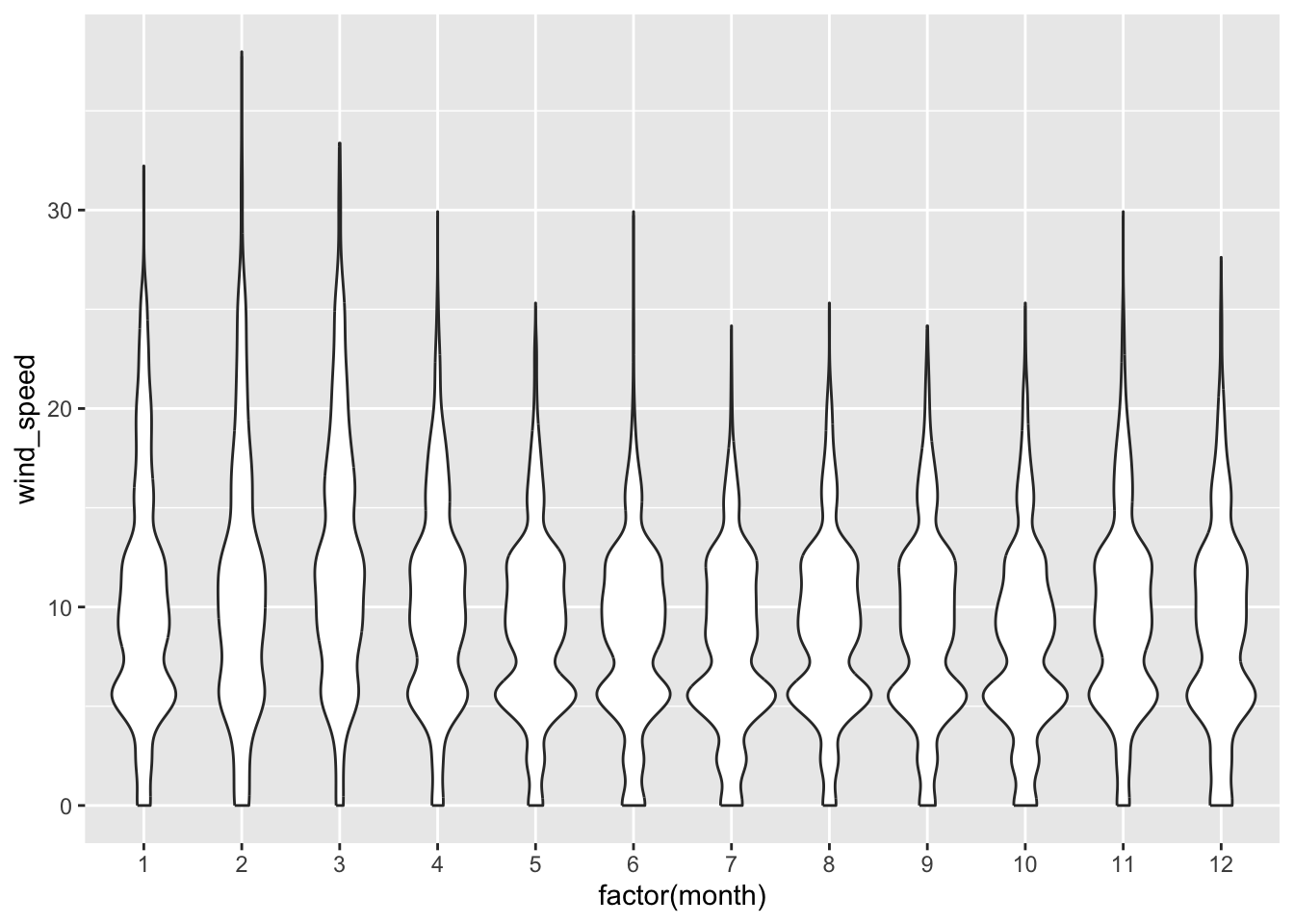
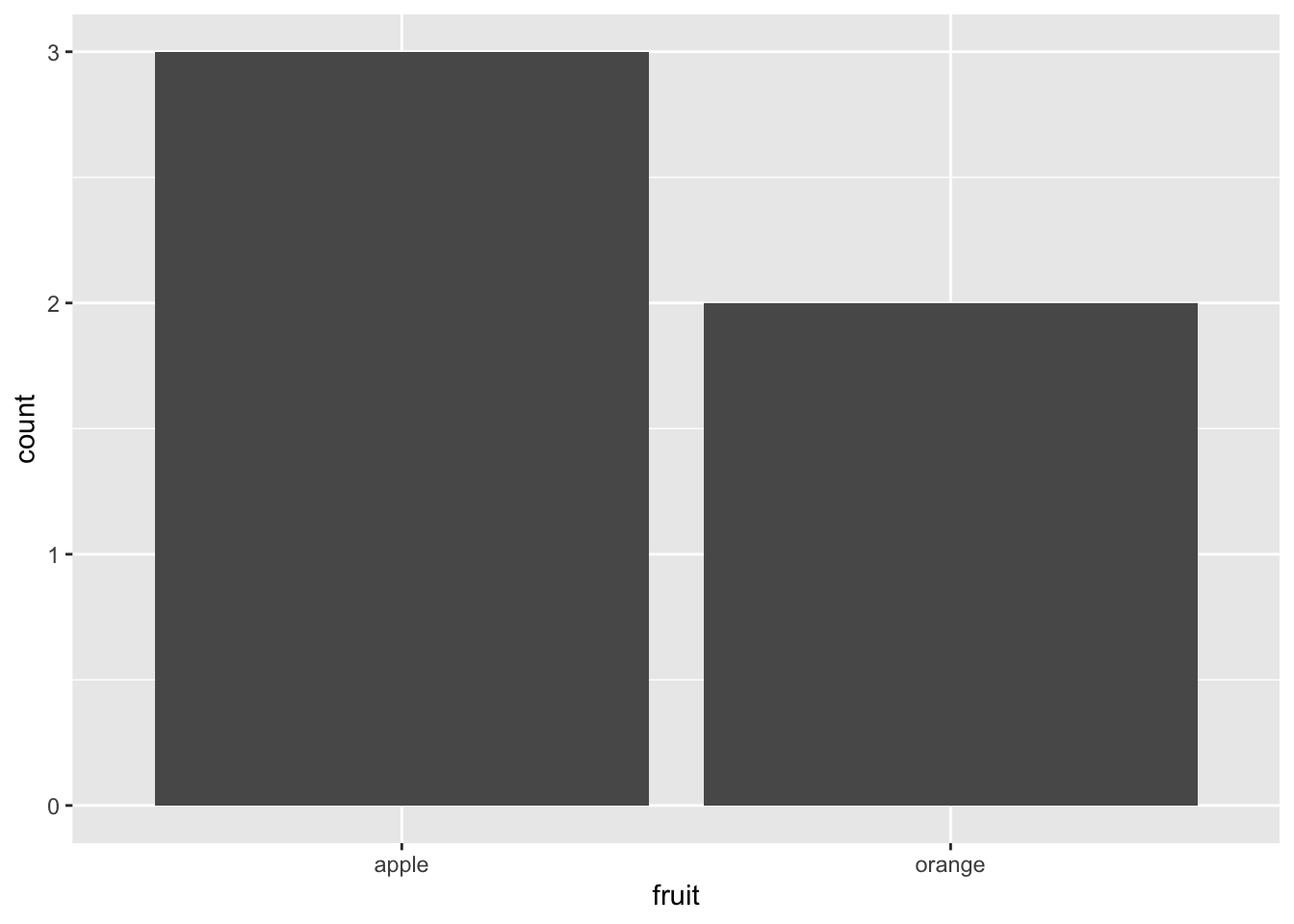
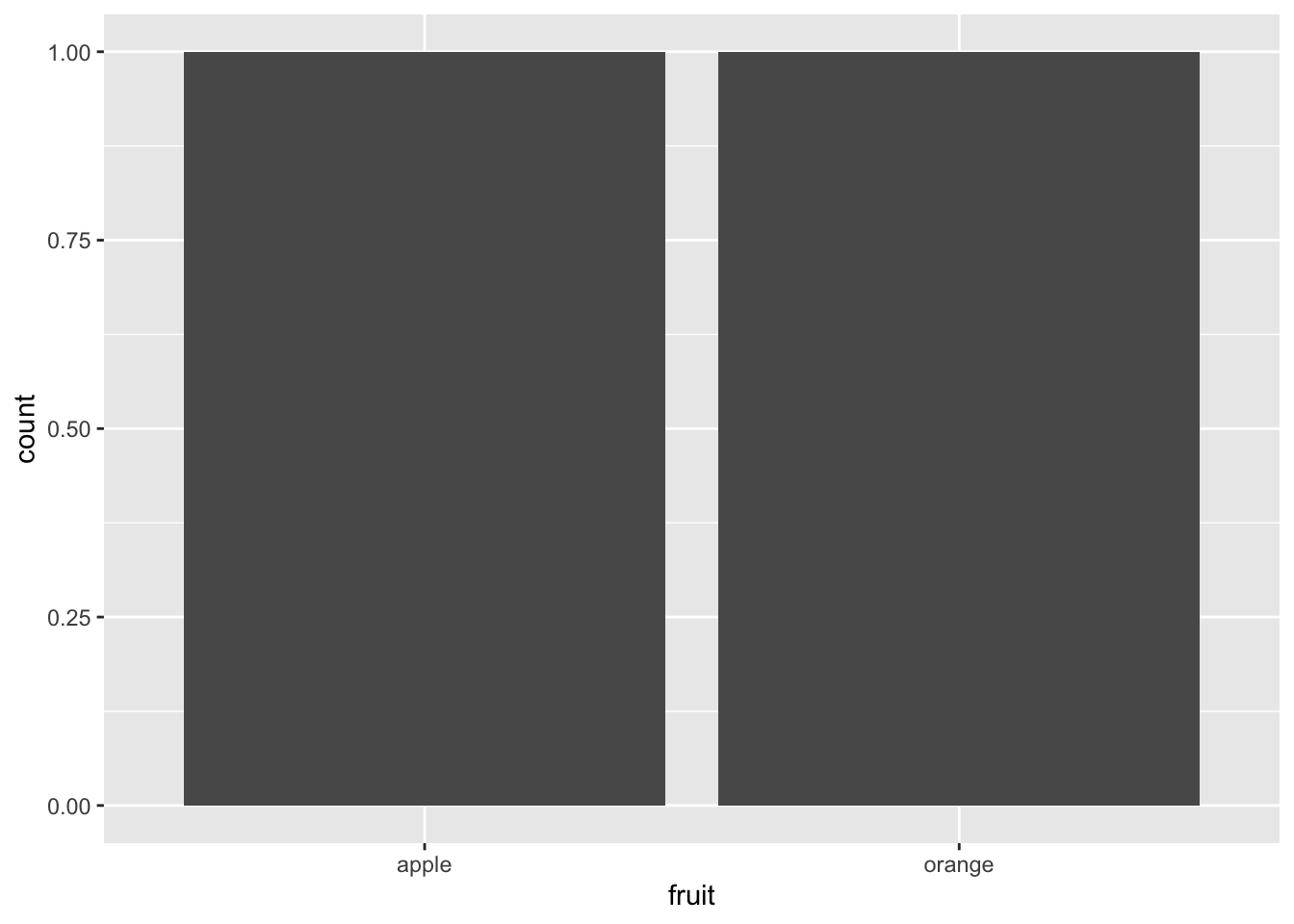
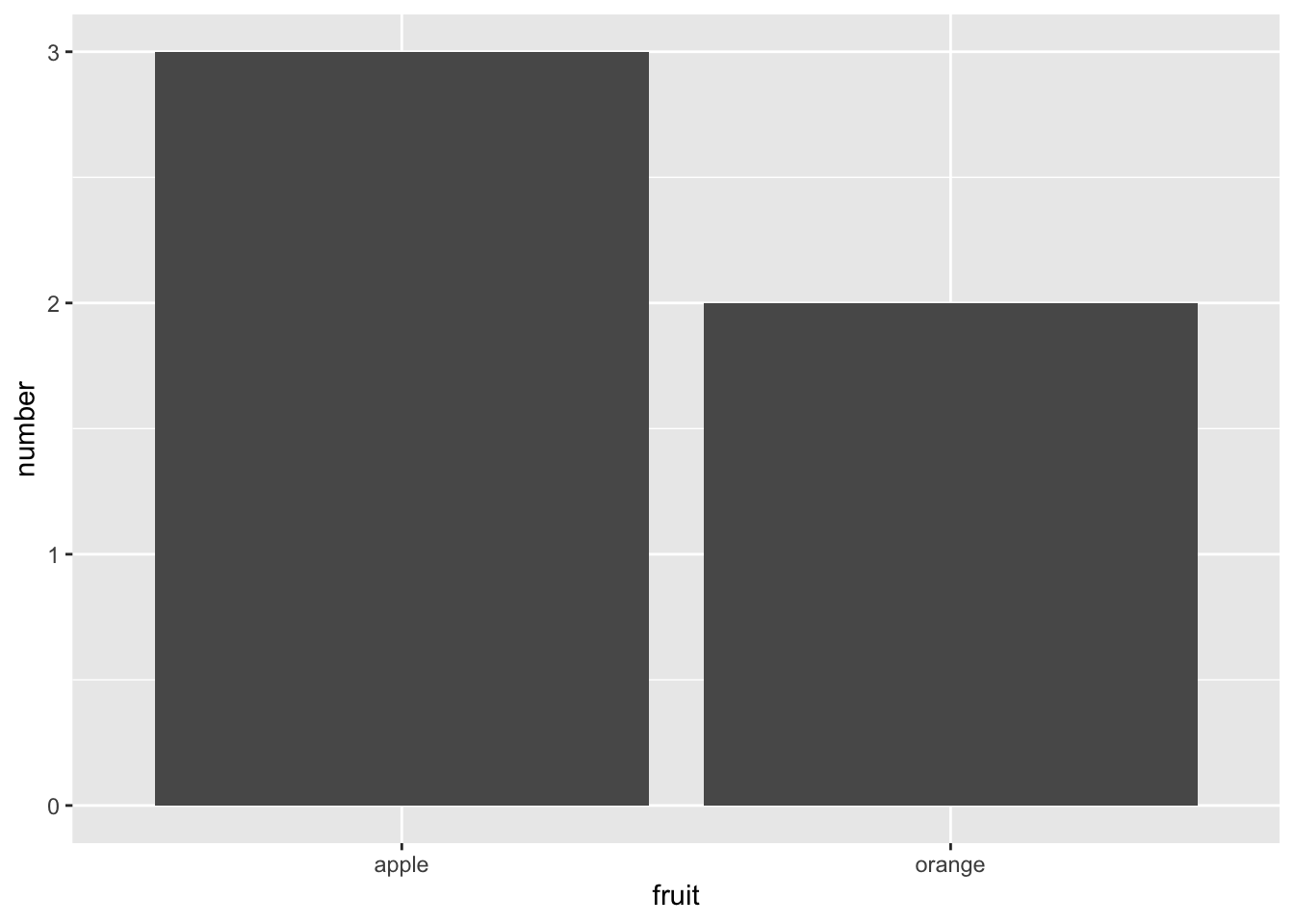
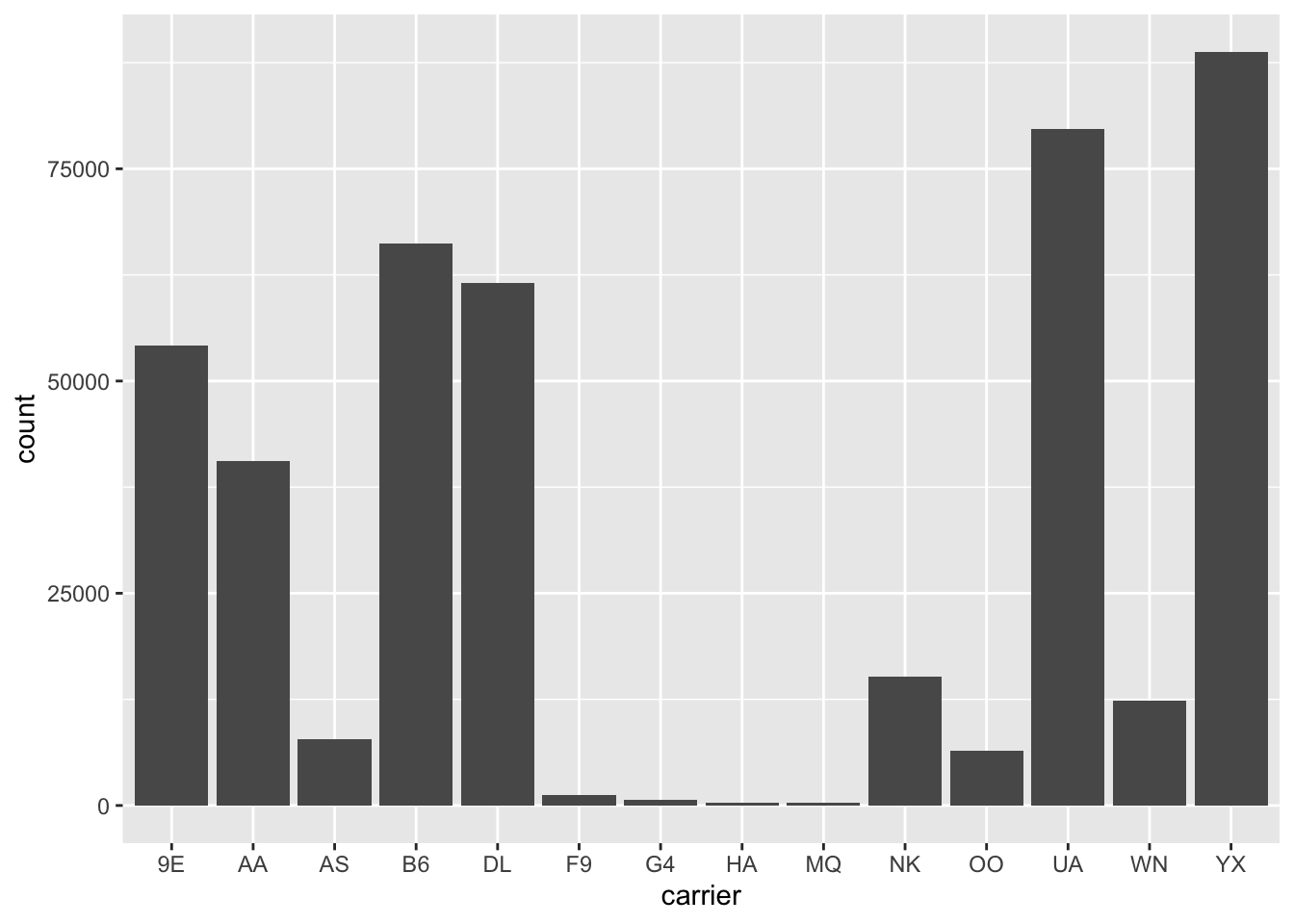
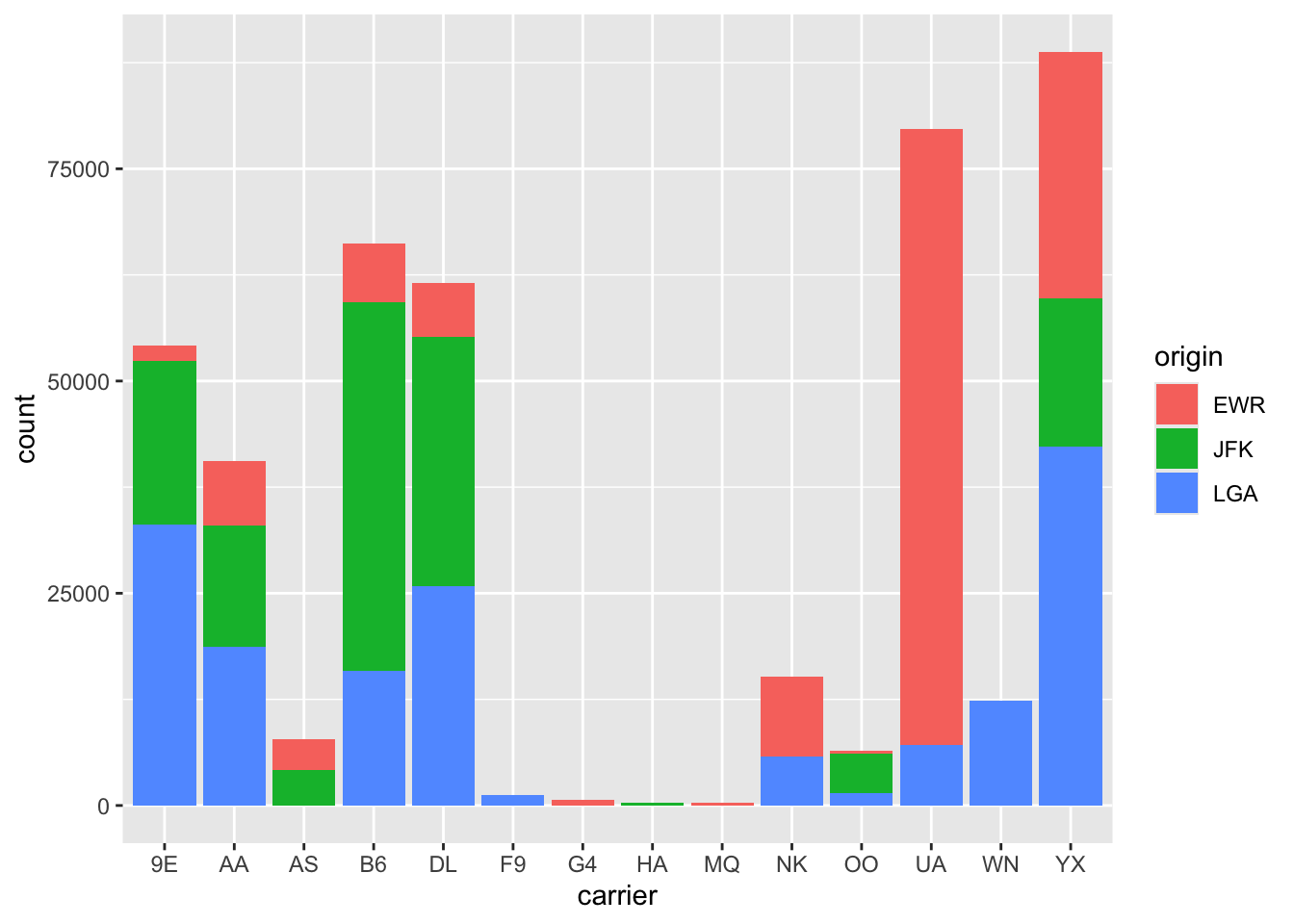
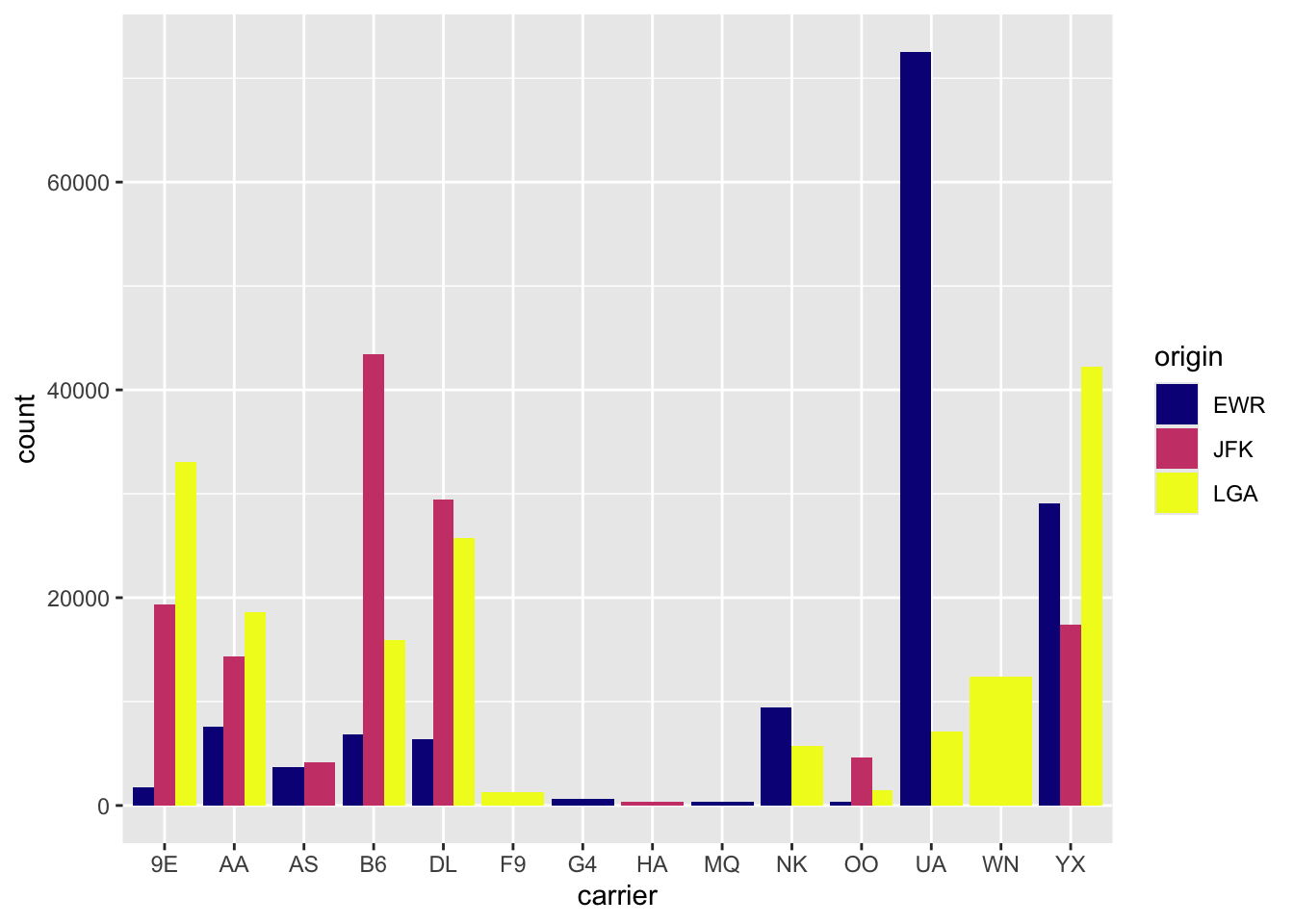
Rows: 26,207
Columns: 15
$ origin <chr> "JFK", "JFK", "JFK", "JFK", "JFK", "JFK", "JFK", "JFK", "JF…
$ year <int> 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023, 2023,…
$ month <int> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,…
$ day <int> 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,…
$ hour <int> 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15, 16, 1…
$ temp <dbl> 48.0, 48.2, 49.0, 49.0, 49.0, 48.0, 46.4, 46.0, 48.0, 47.0,…
$ dewp <dbl> 48.0, 48.2, 49.0, 49.0, 49.0, 48.0, 46.4, 46.0, 48.0, 47.0,…
$ humid <dbl> 100.00, 100.00, 100.00, 100.00, 100.00, 100.00, 100.00, 100…
$ wind_dir <dbl> 0, 190, 190, 250, 170, 0, 250, 230, 260, 250, 240, 260, 260…
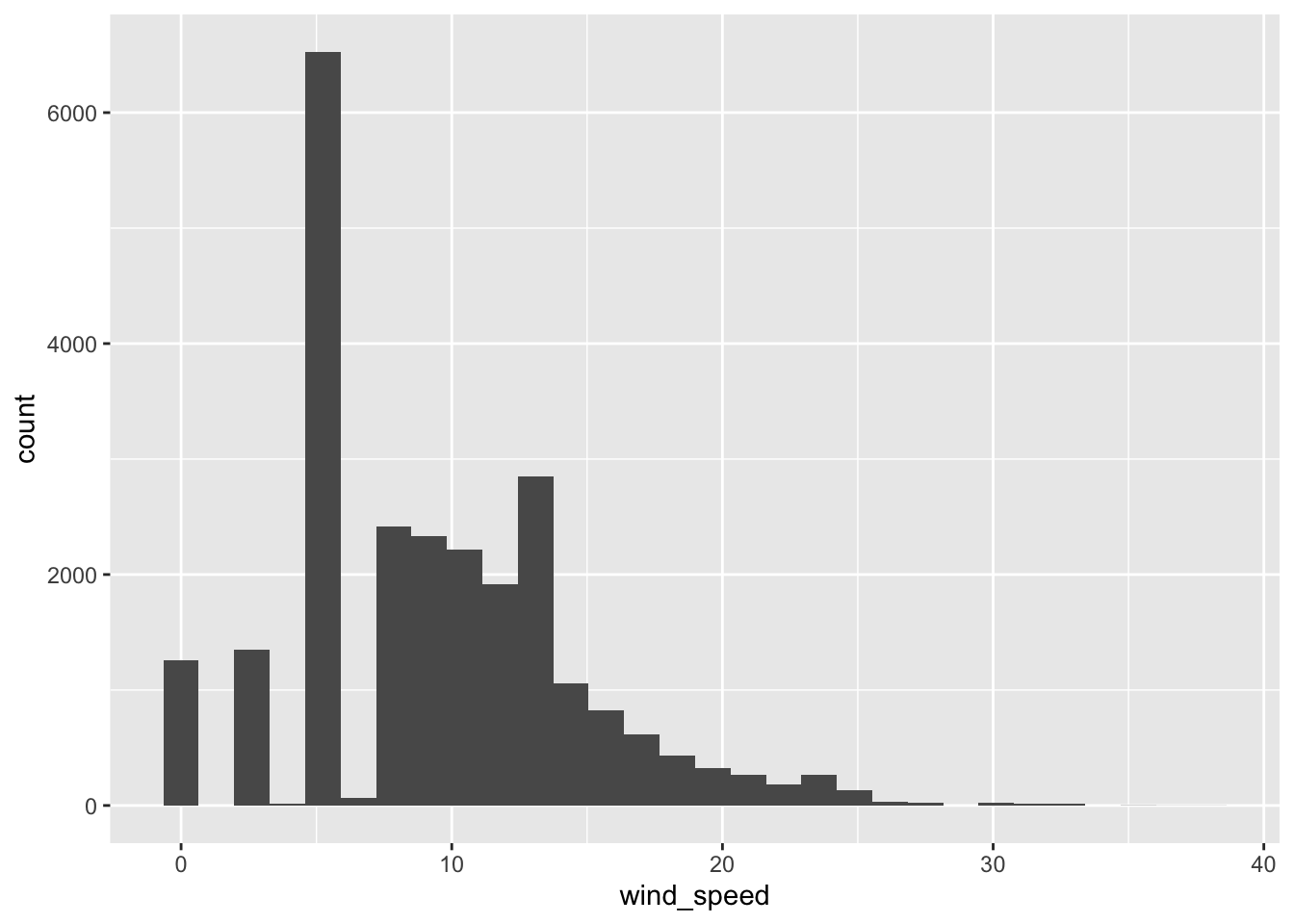
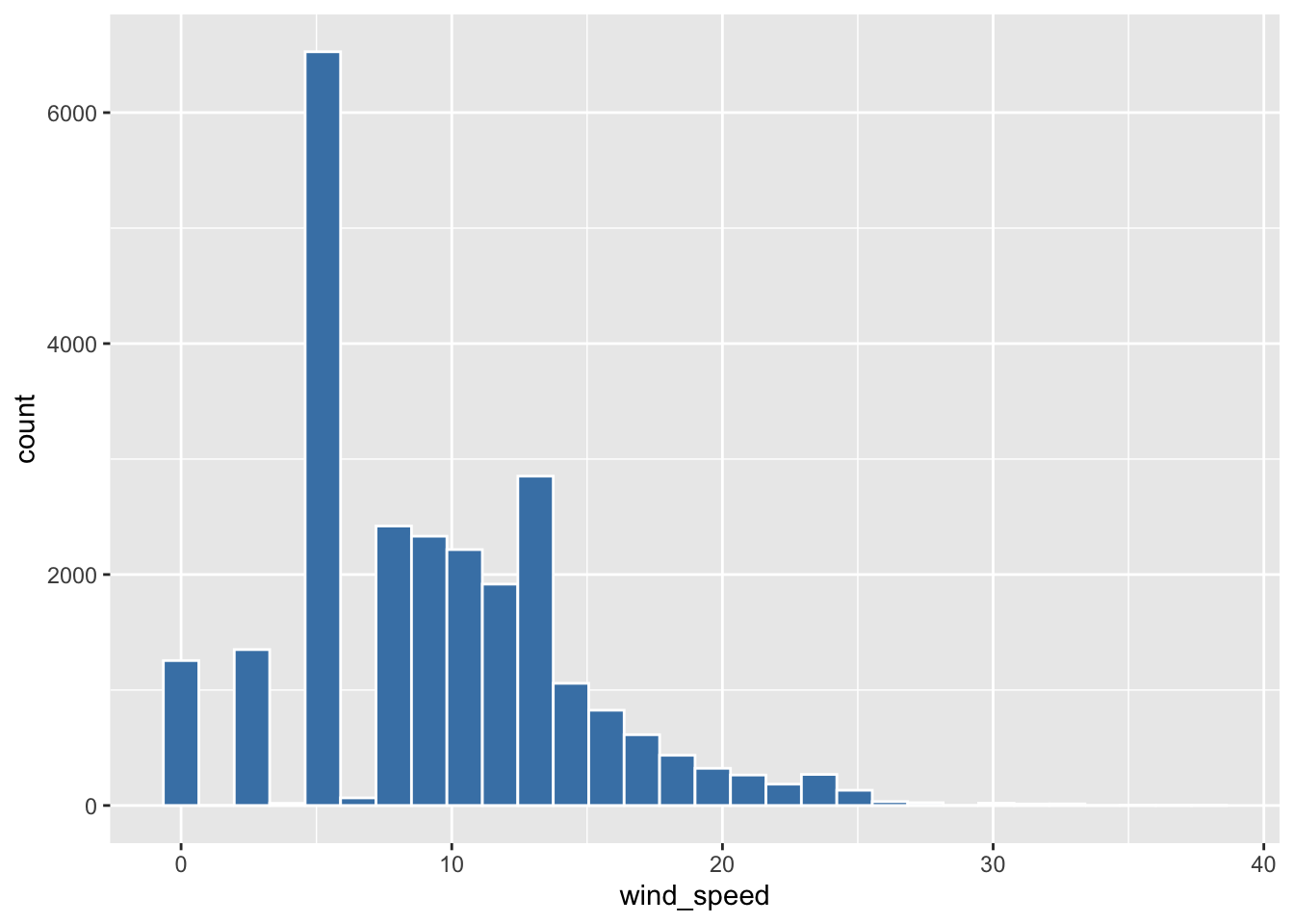
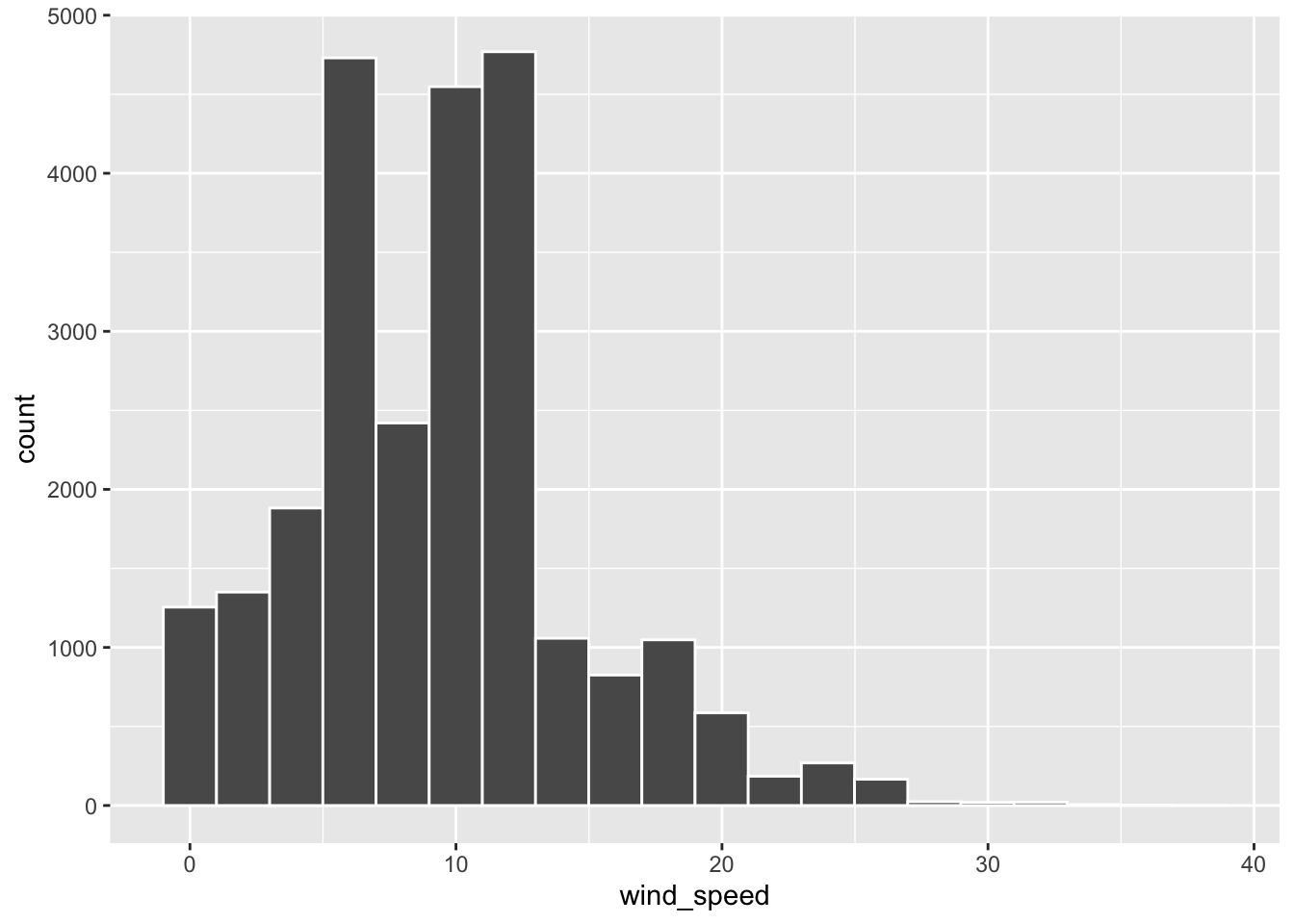
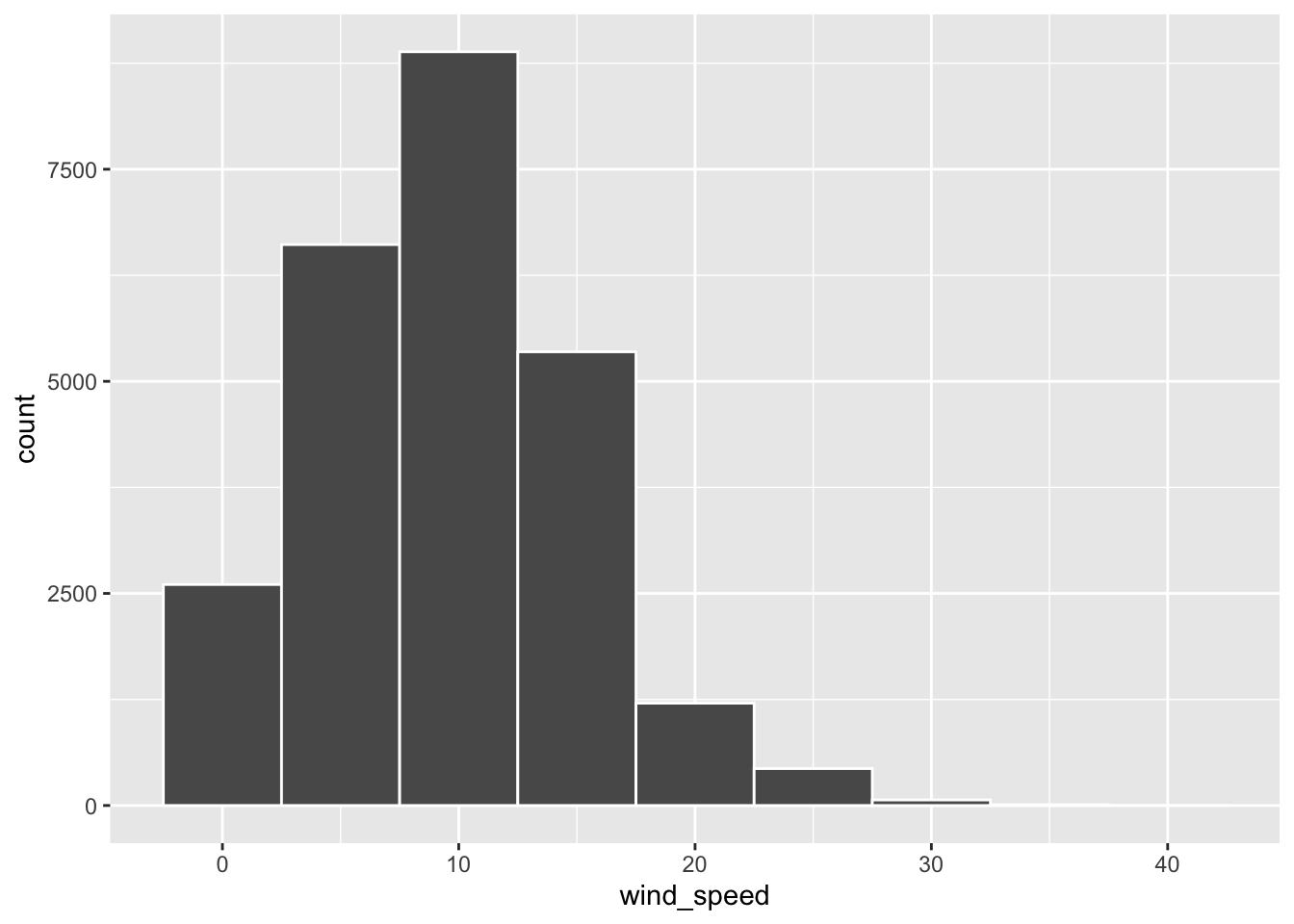
$ wind_speed <dbl> 0.00000, 4.60312, 5.75390, 5.75390, 8.05546, 0.00000, 9.206…
$ wind_gust <dbl> 0.000000, 5.297178, 6.621473, 6.621473, 9.270062, 0.000000,…
$ precip <dbl> 1e-02, 1e-02, 1e-04, 2e-02, 1e-04, 1e-04, 0e+00, 0e+00, 0e+…
$ pressure <dbl> 1010.2, 1009.2, 1009.0, 1008.0, 1007.8, 1007.6, 1007.3, 100…
$ visib <dbl> 0.25, 2.50, 0.25, 4.00, 0.75, 0.75, 0.24, 0.50, 8.00, 5.00,…
$ time_hour <dttm> 2023-01-01 00:00:00, 2023-01-01 01:00:00, 2023-01-01 02:00…